New mediation law passed on 28.11.2019 introducing mandatory mediation is expected to affect fundamentally civil proceedings in the majority of disputes before Greek Courts. The relevant provisions of law 4640/2019 will come into effect gradually beginning 2020 and it remains to be seen whether their mandatory nature will live up its expectations and contribute to higher number of extrajudicial settlements, or whether it will become another formality.
Information obligation
Law 4640/2019 introduces the obligation of the attorney at law of any party seeking recourse to Courts, to inform said party in writing on the option of resolving the dispute, or part of it, through mediation, as well as on the “Mandatory Initial Mediation Session” (see below). This information document is signed by the party and its attorney at law and must be submitted together with the relevant civil action οr the pleadings, otherwise, the case is dismissed on formality grounds. To be noted that the above obligation is effective as of the enactment of the new law, i.e. for all lawsuits filed after 30.11.2019.
Mandatory Initial Mediation Session
In addition, disputes tried under the standard civil procedure (i.e. not preliminary injunctions or other disputes for which a particular statutory procedure is foreseen, such as labor law disputes, disputes from lease agreements etc.) falling under the competence of the Single1 and Multi-Member Court of First Instance and certain family disputes, will have to go through a so called “Mandatory Initial Mediation Session – MIMS”, initiated again by the party seeking judicial recourse, either before or after the filing of the relevant civil action2. If said party fails to do so, the case is not heard by the Court. The timeline of the MIMS is as follows:
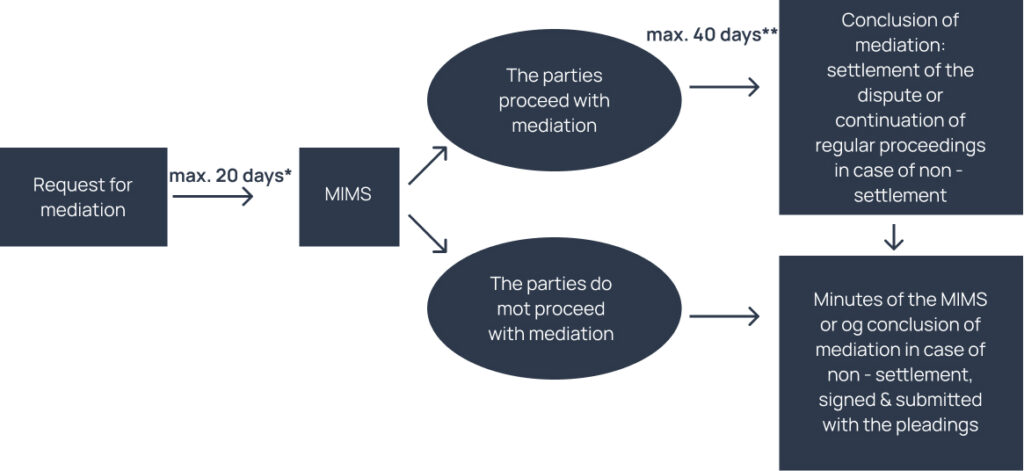
*30 days if one of the parties resides abroad
** Can be extended by the parties. The deadline starts from the lapse of the 20 (or 30) day deadline to hold the MIMS
The new law provides that legal entities may be represented in the MIMS by a special proxy and their attorney while natural persons may be represented only by their attorney at law, in case their presence, either physically or through electronic means, is not possible.
Finally, the law provides for certain monetary penalties in case one of the parties does not appear in the MIMS.
Common provisions for mandatory and voluntary mediation
Initiation of mediation proceedings, whether mandatory or voluntary, results in the suspension of prescription period, limitation time and certain procedural deadlines, which are resumed after mediation is terminated or otherwise concluded.
It should be reminded that mediation proceedings do not prevent parties to seek preliminary relief according to the provisions of the Code of Civil Procedure.
It should be reminded that mediation proceedings do not prevent parties to seek preliminary relief according to the provisions of the Code of Civil Procedure.
Particular attention must be paid to the fact that due to the confidential nature of mediation proceedings, individuals participated therein, cannot be examined as witnesses if the case is brought before Courts or arbitration panels and most importantly they cannot submit information that was brought up during mediation proceedings, or is related with it, such as discussions and proposals made by the parties and the mediator
Finally, the law set outs the details on the procedure of mediation, the Mediation Committee and the mediator accreditation process.
The law came into force on 30.11.2019, however, the provisions on MIMS will apply as from January 15, 2020 for family disputes and as from March 15, 2020 for lawsuits falling under the competence of the Single and Multi-Member Court of First Instance as described above. Update: Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the MIMS procedure will apply as of July 1st, 2020
1 Provided that the monetary value of the dispute exceeds 30,000 EUR
2 Disputes where the State, municipal or prefectural authorities and public entities, are litigant party are exempted from the Mandatory Initial Mediation Session.
© Logaras Law (2023). All contents on this website, including logos, trademarks, texts, newsletters and articles (hereinafter the “Contents”), are protected under intellectual property law. Except where otherwise stated, use, downloading, reproduction and distribution in whatever form and by whatever medium (including Internet) for whole or part of the Contents available on this website and newsletter is not authorized.